The MHRA GPvP inspectorate recently published their latest inspection metrics for the period of April 2014 to March 2015. The full metrics report is available on GOV.UK.
The report concludes that in the period April 2014 to March 2015, MHRA conducted a total of 48 pharmacovigilance inspections. Approximately 29% of these inspections were of marketing authorisation holders (MAHs) that had not previously undergone an MHRA pharmacovigilance inspection. The largest proportion of inspections were performed as routine re-inspections (ie of MAHs who had previously undergone a pharmacovigilance inspection).
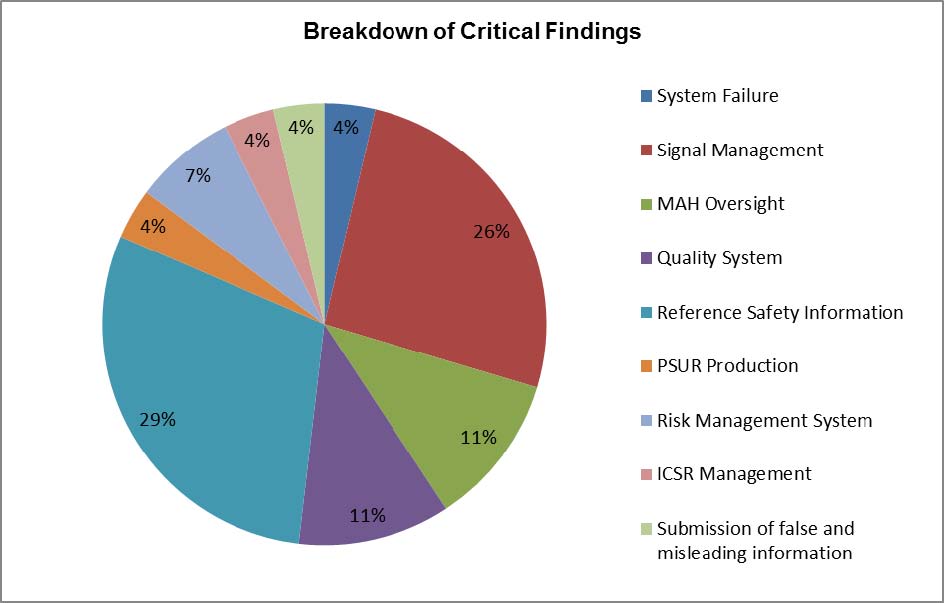
The number of 'critical' findings identified during this reporting period had increased from the previous period, with 27 'critical' findings reported versus 19 in the previous period. The largest proportion of 'critical' findings remained in the topic area of reference safety information, representing 29% of all reported 'critical' findings. 'Critical' findings associated with reference safety information were again characterised by failures and significant delays to submit safety variations to update the safety sections of summaries of product characteristics (SPCs) and patient information leaflets (PILs).
In this reporting period, a sharp increase in the number of 'critical' findings associated with signal management was identified. Seven 'critical' findings were reported and these were associated with:
- failures to conduct signal detection activities
- failures to incorporate all available data into signal detection activities
- significant delays in completing signal evaluation
- failures to address previously reported major inspection findings, resulting in an escalation of the issue (persistent non-compliance)
In some instances, the persistent non-compliance had had a measurable impact, ie subsequent completion of signal detection activities had resulted in new signals being identified and updates to product information.
The number of 'major' findings associated with the pharmacovigilance master file has decreased from the previous period by approximately 45%. Additionally, the number of 'critical' and 'major' findings reported in association with deficiencies in the collection of data from non-interventional programmes has decreased from the previous period. The topic areas representing the largest proportions of inspection findings remain associated with key pharmacovigilance activities and outputs such as individual case safety report (ICSR) management, signal management and reference safety information.
I hope that you are able to use these findings to make improvements within your own work or organisation and we would welcome hearing about if you find the report useful.
Don’t miss the next blog, sign up to be notified by email when a new post comes out.
Check out our guidance on good practice for information on the inspection process and staying compliant.

